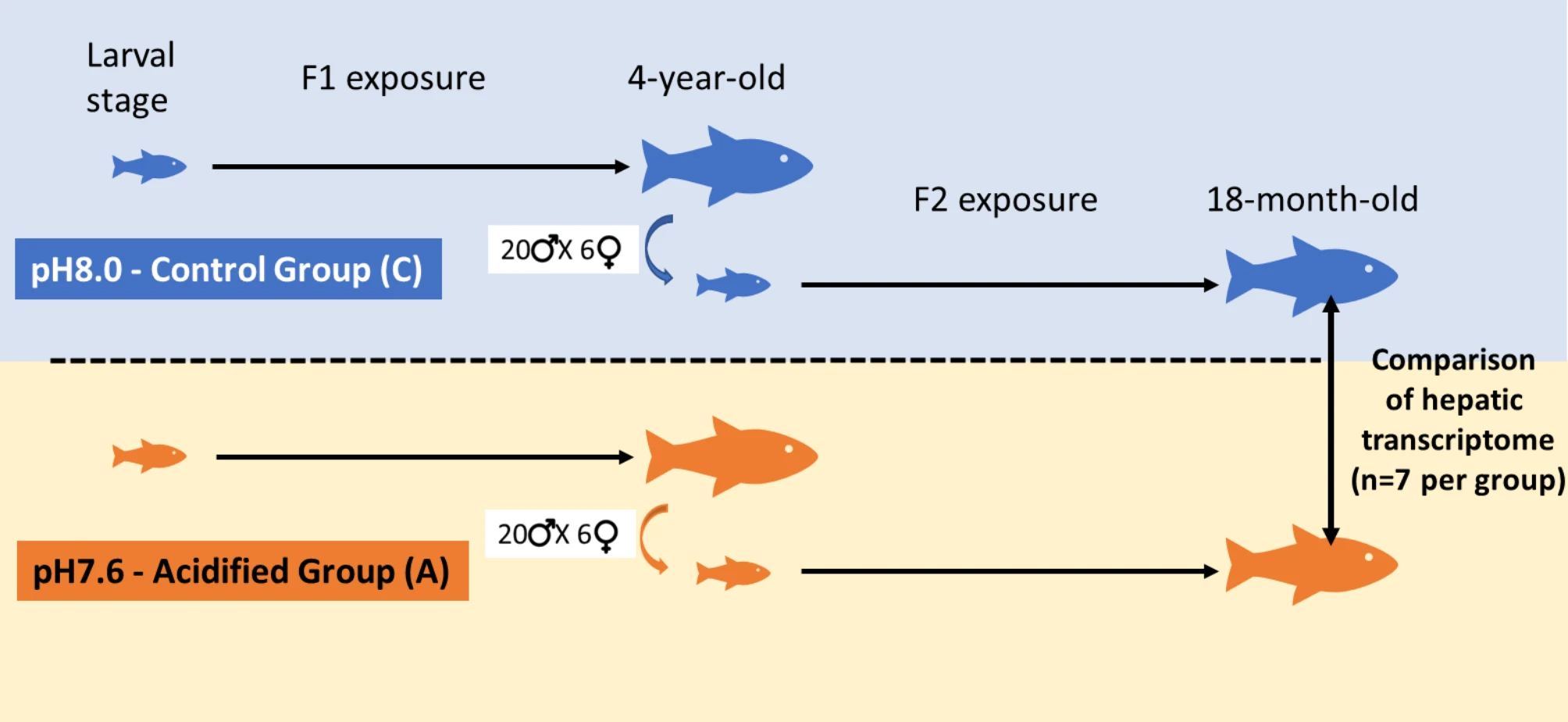
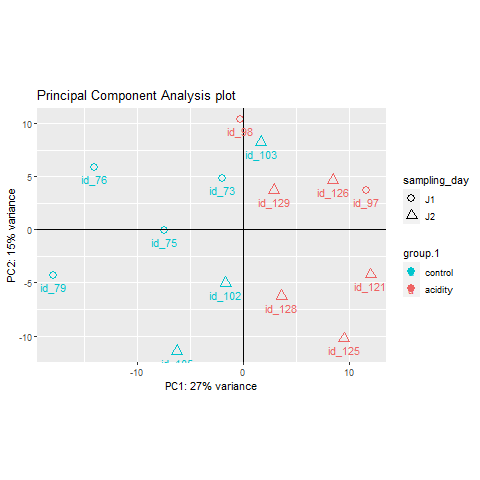
Support information
- Category: Transcriptomics
- Coordinator: SeBiMER
- Project example: LIVACID
Transcriptomics
RNA sequencing, also known as RNA-Seq, is a widely used technology that enables the capture and quantification of all RNA molecules present in a single cell or a population of cells under specific conditions. One of the primary objectives of RNA-Seq is to profile gene expression by identifying differentially expressed (DE) genes or molecular pathways between two or more biological conditions. Additionally, RNA-Seq can be employed to identify various features within a genome, such as novel isoforms and alternative splicing, non-coding RNAs, single nucleotide variations, and fusion genes. The key steps in the bioinformatics pipelines used for analyzing RNA-Seq data encompass data quality control and trimming, mapping to a reference genome or de novo transcriptome assembly, and potentially performing feature counting and statistical normalization before conducting differential expression analysis.